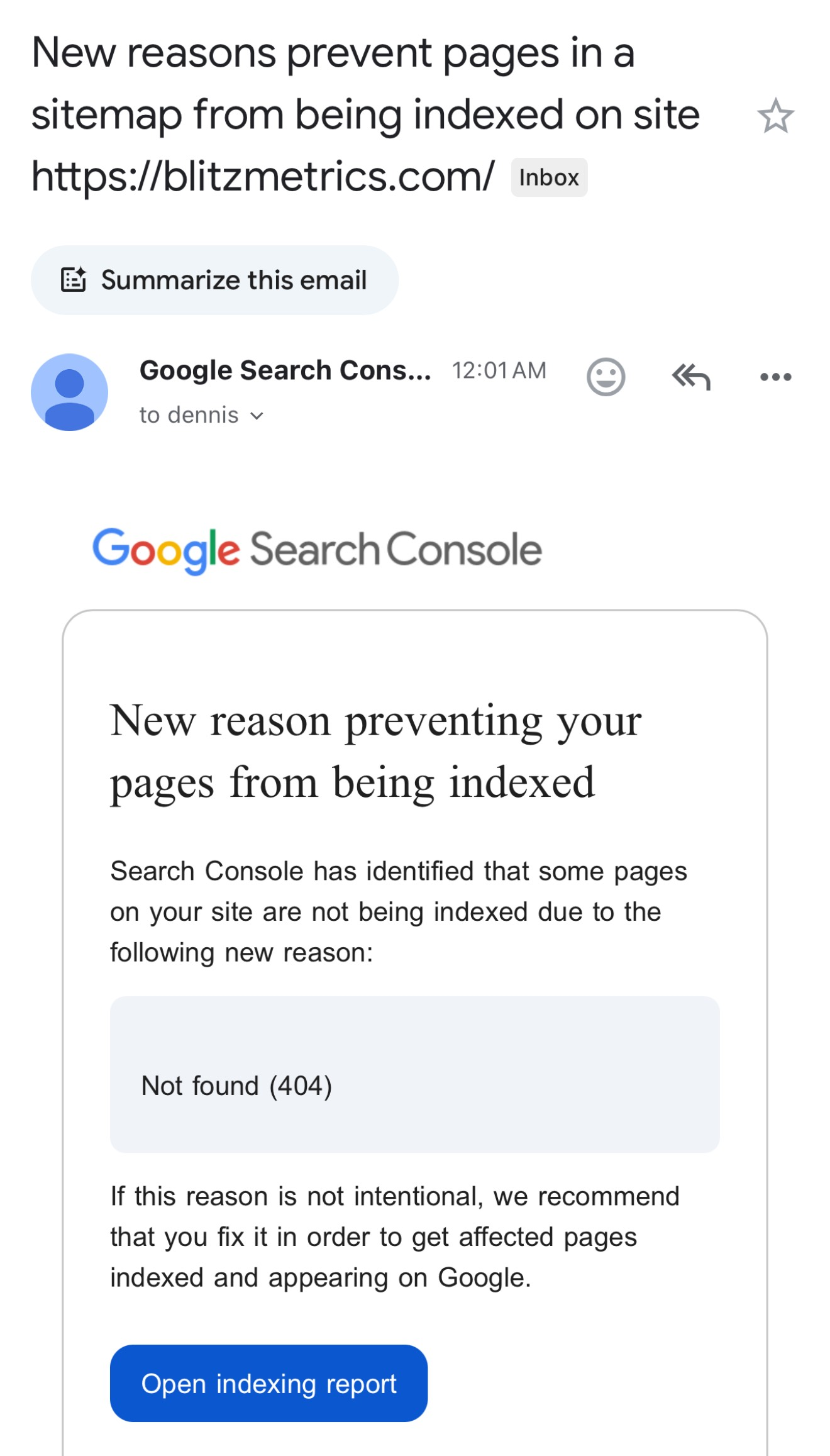
404 errors occur when users land on non-existent pages — either on your site (due to broken or removed pages) or external sites you link to.
These errors harm user experience and SEO, making their resolution a critical part of website maintenance.
For instance, 876 visitors hit a 404 page on our site last month alone. That’s 876 missed opportunities to engage with potential leads.
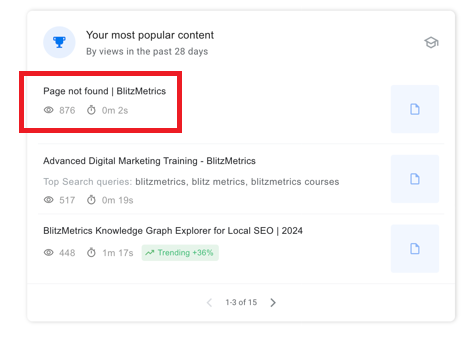
Why Fixing 404 Errors Is Essential for Ongoing Site Maintenance
Imagine nearly 900 people coming to your store, but nobody is there. Each month. That’s a lot of missed opportunities — clients you’re turning away or money that could be in your bank account. And nearly all of us suffer from this same issue. Fixing these errors ensures you retain traffic, improve SEO, and avoid turning away potential clients.
Resolving 404 errors is straightforward when you know the steps. Here’s how to do it effectively.
Task Checklist
Tools You’ll Need:
- Google Search Console (GSC) for identifying internal errors.
- Ahrefs or Broken Link Checker for external link audits.
- RankMath SEO plugin for resolving issues with redirects.
Steps Overview:
- Identify internal 404 errors using GSC.
- Identify external 404 errors using link-checking tools like Ahrefs.
- Fix internal errors with 301 redirects (using RankMath SEO).
- Resolve external errors by updating or replacing broken links.
Estimated time it takes to identify and fix 404 errors is approximately 1 to 3 minutes.
Step 1: Identify 404 Errors
Every month, Google Search Console sends you a report showing how your site is performing. The report highlights your top-performing content and also flags issues like 404 errors. Google Search Console is the best tool to identify 404 errors because it uses Google’s own data and provides accurate insights into your website’s performance. You’ll get a report for every site you manage.
You can also visit Google Seach Console to see detailed insights about traffic, site errors and so on.
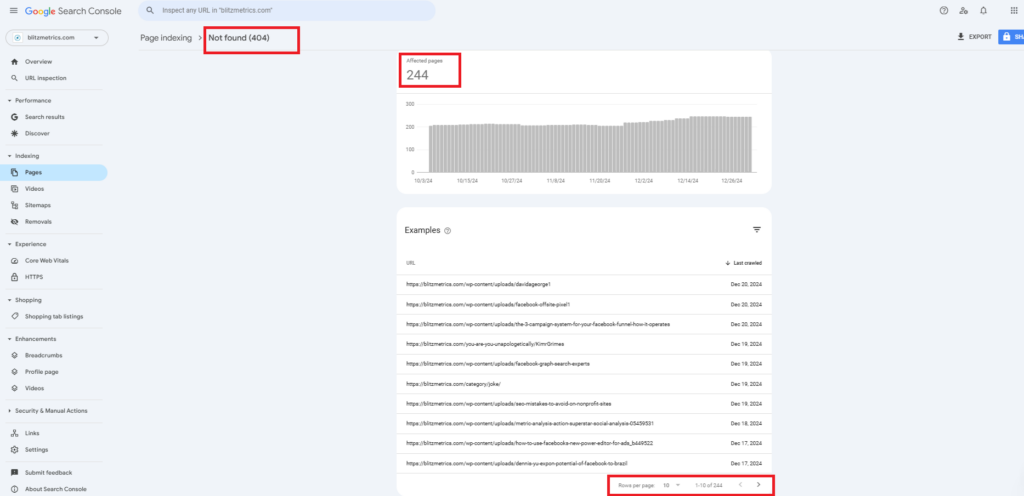
Log in to Google Search Console. Click “Pages” and select “Not Found (404).”
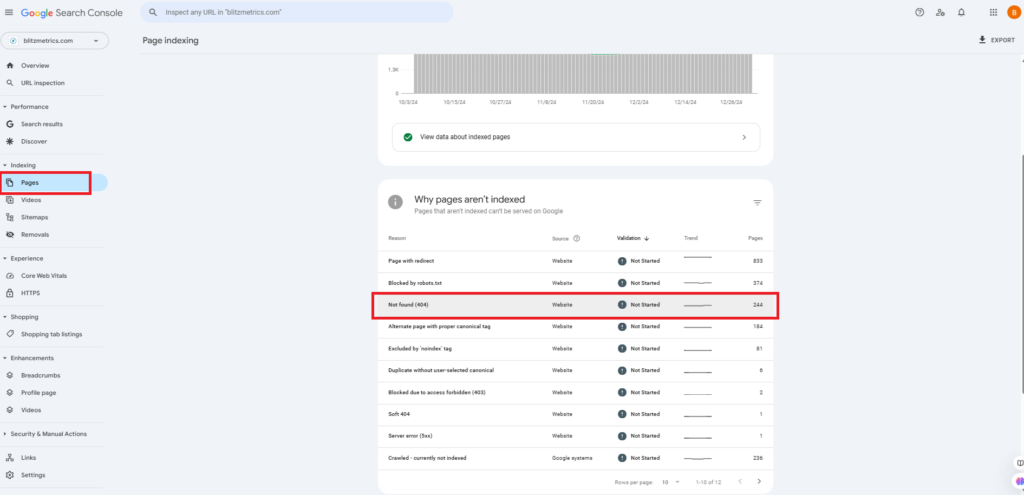
Review the list of flagged URLs:
Step 2: Resolve Internal 404 Errors
We resolve internal 404 errors using a WordPress plugin called Rank Math SEO by setting up 301 redirects from the broken or non-existent page URLs.
What is a 301 Redirect?
A permanent redirect from one URL to another, ensuring SEO value and user experience are preserved.
For example, if visitors were landing on a missing page related to “becoming a virtual assistant,” we’d ensure those users are redirected to the correct or most relevant content.
Here is how to set up the redirect:
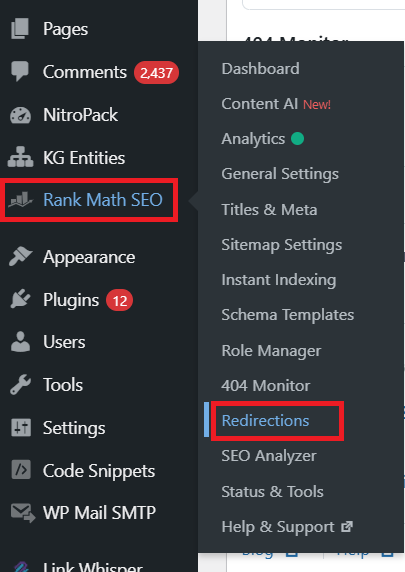
1. Go to Rank Math SEO’s “Redirections” page:
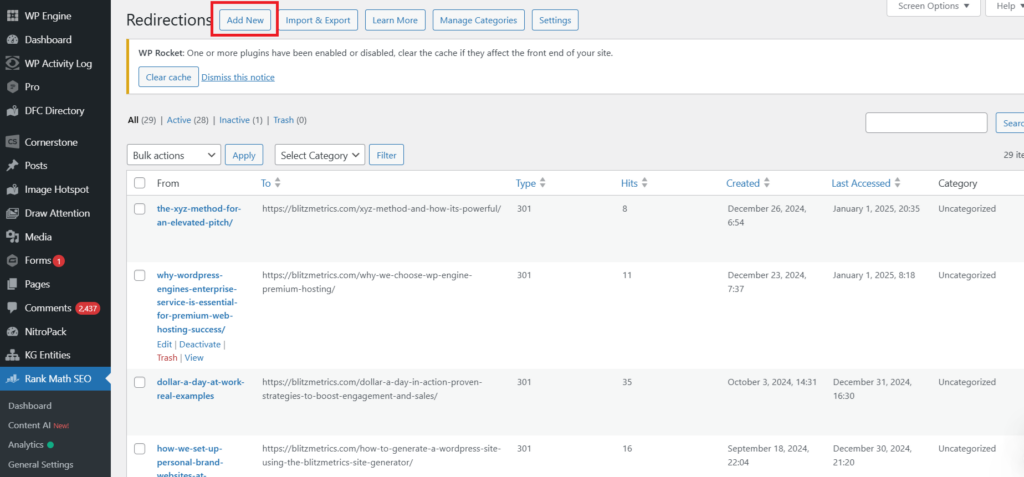
2. Then click on “Add New”
3. Enter the old (broken) URL in the “Source URL” field. Enter the new URL in the “Destination URL” field.
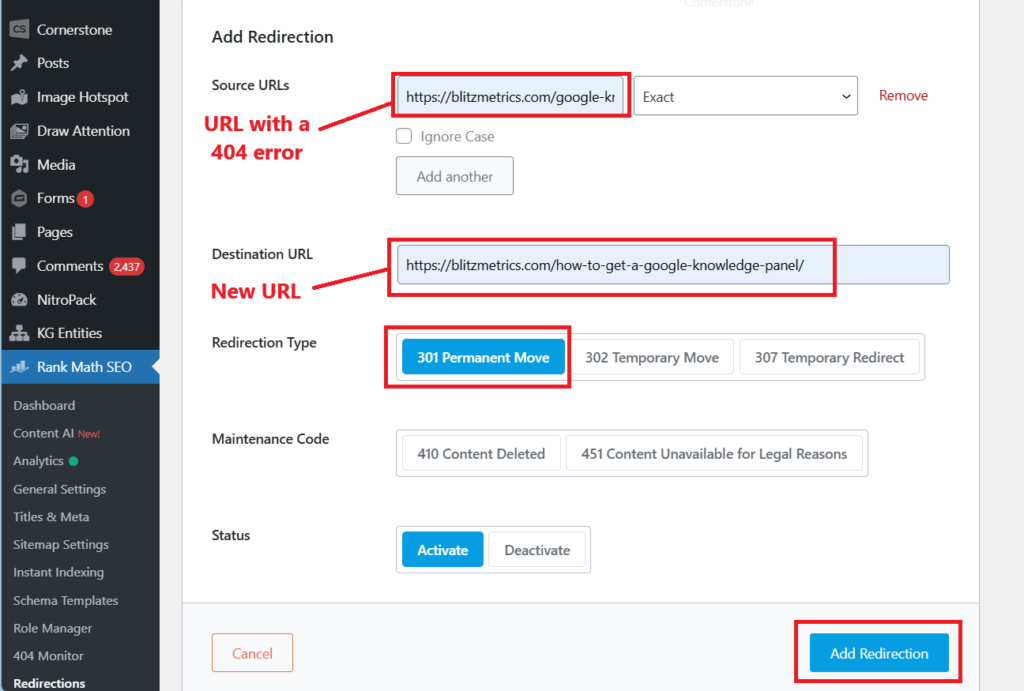
4. Make sure that the redirection type is “301 Permanent Move.” Then click “Add Redirection”
Step 3: Identify External 404 Errors
Broken external links occur when you link to resources on other websites that are outdated or removed. Use tools like Ahrefs or Broken Link Checker to scan your site for outbound links pointing to 404 errors.
Step 4: Resolve External 404 Errors
- Identify the problem links:
Use the external link audit tools like Ahrefs or Broken Link Checker to find broken outbound links. - Contact the external website:
Notify the site owner about the broken link and request an update or replacement URL. - Update or remove the link:
If the resource is no longer available, replace it with a relevant, up-to-date link. If no alternative exists, consider removing the link altogether. - Set up a custom redirect (optional):
If the external resource is crucial, create a page on your site that explains the situation and provides alternative information or links.
That’s it. You’re done!
If you enjoyed this tutorial, be sure to explore our Task Library for additional tasks waiting to be mastered!
Verification Checklist
After fixing 404 errors:
- Test internal redirects: Visit old URLs to confirm they redirect correctly.
- Monitor in GSC: Ensure flagged errors no longer appear under “Not found (404).”
- Validate external links: Re-scan your site to confirm all outbound links are functional.
